Part
01
of one
Part
01
Edge AI Computer Vision - Training Use-Case
Key Takeaways
- The top five use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision that solve labor or skill shortages are robotic automation, additive manufacturing, machine vision, product optimization, and remote monitoring.
- Nine startups or companies working in the Edge AI Computer Vision space are Keyence, FLIR Systems, Cognex, Antares Vision Group, Omron Automation, Tulip, Osaro, and Landing AI.
- The IBM Global AI Adoption Index for 2022 states that 22% of respondents to the survey are adopting AI into business operations because of skills or labor shortages.
- According to McKinsey, along with robotic process automation (39%), computer vision (34%) is one of the most commonly deployed AI capabilities.
- According to Thomas, an "industrial sourcing platform and marketing powerhouse," three manufacturing personas influencing the buying process are Design Engineers, Procurement Managers, and MRO Managers.
Introduction
In this brief, five use cases were identified for Edge AI Computer Vision that addresses the skill/labor shortages. These are robotic automation, additive manufacturing, machine vision, product optimization, and remote monitoring. The market opportunity, with triangulations for market value and total VC investments, current manual training processes, buying persona, decision-makers, startups or companies, and industries were identified for the training use case for Edge AI Computer Vision.
Publicly available information that specifically addressed this use case was limited in the public domain for this report's market value, buying persona, and VC investment criteria. Where this occurred is identified in the body of the report under the relevant section and addressed in the Research Strategy section, where explanations for the triangulations used in the report are also provided.
Finally, this spreadsheet provides information regarding the startups/companies that are operating similarly to Invisible.ai, Retrocausal, and Drishti.
1. Top 5 Use Cases for Edge AI Computer Vision for Solving a Skill/Labor Shortage
- Precompiled data regarding the top 5 use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision for solving a skill or labor shortage is not publicly available. The use cases provided here were identified as top use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision by industry publications or practitioners, cross-referenced by articles on how AI can address labor shortages.
- Five use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision that can address the labor/skills shortage are robotic automation, additive manufacturing, machine vision, product optimization, and predictive maintenance.
- Given the focus on manufacturing for this research project, and the labor force shortage for manufacturing as illustrated by the image below, the examples provided for each use case will focus on manufacturing, however, the overall use case can be applied across a number of industries.
Robotic Automation
- Robotic Automation refers to using robots to perform "repetitive tasks that a human would, freeing human employees from mundane, repetitive work."
- Computer vision assists the robots in grasping and manipulating objects, while autonomous guided vehicles can assist with mapping, object avoidance, surface anomaly detection, and transporting parts and goods.
- The benefits of deploying robotic automation include labor cost savings of 75%, assisting with injury avoidance at the assembly line, handling heavy or dangerous materials, conducting repetitive movements, and allowing for 24/7 production.
- Providers of robotic automation using Edge AI Computer Vision include ABB, Aethon, and Fanuc.
Additive Manufacturing
- Additive manufacturing is a computer-controlled process for creating 3D objects, i.e., 3D printing.
- AI allows for inputting design parameters and determining the most "efficient, effective, and manufacturable options." After design selection, AI predicts, monitors, and eliminates product defects.
- At Irida Labs, Edge AI Computer Vision is used in Laser Process Monitoring, an automated quality assurance product used in additive manufacturing.
Machine Vision
- Machine vision refers to the use of AI and computer vision to recognize shapes and their orientation and status in varying lighting conditions. Essentially, machine vision can be applied in any part of the QA process that would usually use humans.
- The previous report on Edge AI Computer Vision identified one specific application of Machine Vision, in the form of Factory Automation, however, machine vision can also be applied to "packing, palletization, and cargo loading, saving labor, time and money."
- At RobotIQ, customers such as Nestle, Pepsico, Kerry, Johnson & Johnson, and P&G are using the palletizing solution.
Product Optimization
- The production optimization use case refers to using Edge AI Computer Vision to "monitor temperature, humidity, and running variances for different products and materials, so that production machines can be optimized based on current conditions."
- Using Edge AI Computer Vision for product optimization helps manufacturers to "connect and manage the entire end-to-end manufacturing process from design to demand planning and material inventory, to energy consumption to endgame logistics."
- Mindsphere from Siemens is an industrial IoT as a service solution Rittal used for conditional monitoring and asset management. Cooling solutions communicated with the production environment to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprints by up to 75%.
Remote Management
- The remote management solution refers to using IoT solutions to "remotely monitor and manage equipment in factories, farms, hospitals, oil wells, and other locations."
- NVIDIA Fleet Command is one product with remote management capabilities. The system allows users to view "system information or data, navigate directories, view logs, and more" without requiring physical access to the network or the system.
- Puraset is a company based in Hungary that is working towards making clean drinking water available to more people. Using AWS IoT, it connects its PurAID units to an operation center from where it remotely manages, in real-time, the equipment, water volume, and quality.
- This use case implies positive scalability, as Puraset plans to install its units across the globe.
2. Analysis of Training Use Case
2.1 Market Opportunity
Market Value — Triangulation for AI-Powered Training for Edge AI Computer Vision.
- Market values for AI-powered training programs for Edge AI Computer Vision targeted at training, on-demand coaching, or assessments of new or existing employees in a production environment are not publicly available. The research path used to determine this is outlined in the Research Strategy Section below.
- The 2022 AI Index Report from the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial intelligence (HAI) reports that computer vision capabilities have been embedded into standard business processes across all industries at a rate of 23%, (see the second image in the section below titled AI-Adoption in Human Resources and Manufacturing by Industry) and AI adoption in manufacturing has occurred at a rate of 12% (see the third image in the section below titled AI-Adoption in Human Resources and Manufacturing by Industry).
- The Edge AI market was valued at $15.6 billion in 2022, with a forecasted rise to $107.47 billion by 2029. CAGR is forecasted to be 31.7% during the period 2022-2029.
- Given that computer vision is embedded across all industries at a rate of 23%, the AI Adoption rate across all industries for manufacturing is 12%, and the current market value of the Edge AI market is $15.6 billion, a triangulation of the AI-powered training market for Edge AI Computer Vision results in a value of $430 million.
- Calculation:
- Market Value for Edge AI Software * AI Adoption Rate in Manufacturing = Edge AI in Manufacturing
- Edge AI In Manufacturing = $15.6 billion * 12% = $1.872 billion
- Edge AI in Manufacturing * Embed rate for Computer Vision (Across all Industry) = Estimated Market AI Training in Edge AI Computer Vision
- $1.872 billion * 23% = $430 million.
- The embedded rate for computer vision and the AI adoption rate for manufacturing was used as a proxy for the potential market across all industries for Edge AI Computer Vision. The calculation was performed on market values for the Edge AI market given that this is the specific use case requested.
Market Value — Related Markets
- The market values for AI in Education, AI in Manufacturing, and AI in Computer Vision are below.
- The AI in the Education market (2022 value -$4 billion, CAGR 2023-2032 - 10%) in 2022) did not specifically address Edge AI Computer Vision, nor did it provide any analogous content that could be used as a proxy for AI-powered Training for Edge AI Computer Vision. By application, AI smart content creation using "robots, audio & vision, and 2D -3D visualization" has a 15.9% market share or a market value of $636 million.
- Regarding AI in Manufacturing in 2021, the market was valued at $1.482 billion in 2021, with a forecasted rise to $17.9 billion in 2028. The CAGR during the forecast period of 2022-2028 is 51.5%.
- The market for AI in Computer Vision was valued at approximately $9.15 billion in 2020. During the forecast period of 2021-2027, the market is expected to grow at a CAGR of roughly 39.58%. The market is estimated to be valued at $83.6 billion by 2028.
AI Adoption Drivers
- The IBM Global AI Adoption Index for 2022 states that 22% of respondents to the survey are adopting AI into business operations because of skills or labor shortages.
- Additional reasons for AI adoption are listed below.
- Accessibility — 43%
- Process automation and cost savings — 42%
- Embedded AI in off-the-shelf business applications — 37%
- Competitive (31%), consumer (25%), and environmental (20%) pressures.
- Leadership Directive (23%) and company culture (22%)
- The top three AI investments into 2023 were in research and development (44%), residing AI into current processes and applications (42%), and reskilling and workforce development (39%).
- Giving employees back their time to enable a shift to focus on higher-value work (39%) and addressing the skills' gap (27%) were among the reasons organizations utilized automation tools and software.
- Human resources or employee services was a consideration at 28% of companies using or considering using natural language processing (NLP) solutions.
- The PwC 2022 AI Business Survey indicates that 37% of leaders in AI adoption and 17% of other companies derive value from AI used to improve employee experience and skills acquisition.
- In terms of improving retention and recruitment, 24% of leaders and 15% of other companies derive value from AI deployment in this area.
- The PwC AI Business Survey also indicated that 46% of AI adoption leaders and 24% of other companies intend to use AI to support business decisions impacting the workforce, including diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) measures.
- Thirty-nine percent of AI Adoption leaders and 35% of other companies plan to use AI simulations to hire and train employees.
Barriers to AI Adoption
- "Limited AI skills, expertise or knowledge" is the number one barrier to AI adoption, according to 34% of respondents to the IBM AI Adoption Index 2022 survey.
- Additional barriers indicated were cost (29%), a lack of tools or platforms for model development (25%), complex or difficult-to-integrate and scale projects (24%), and high data complexity (24%).
- Nineteen percent of respondents indicated that their organizations did not have employees possessing the right skill to fully utilize "new AI and automation software and tools."
AI User Groups at Organizations Currently
- Based on responses to the IBM AI Adoption Index 2022, which polled 7502 businesses globally, IT professionals (54%) remain the top users of AI in organizations, followed by data engineers (35%) and developers and data scientists (29%). The professional groups rounding out the top ten are listed below.
AI-Adoption in Human Resources and Manufacturing by Industry
- AI-enabled human resources have been adopted by approximately 9% of all organizations across all industries. In terms of the manufacturing function, it has been adopted by 12% of all organizations across all industries. (See page 161 of HAI 2022 AI-Index Report)
- Industries leading in the adoption of AI-enabled human resources are business, legal, and professional services (14%), automotive and assemble (11%), and financial services (10%). Adoption rates in other industries can be seen in the graphic below.
- For manufacturing, the adoption of AI-enabled manufacturing functions as led by automotive and assembly (26%), consumer goods/retail (18%), healthcare systems/pharma and medical products, and high/tech/telecom (11% each). Adoption rates for different industries can be seen in the graphic below.
- According to McKinsey, along with robotic process automation (39%), computer vision (34%) is one of the most commonly deployed AI capabilities.
- Another AI capability that has been embedded into the product or "business process in at least one function or business unit" related to the training use case in manufacturing is transfer learning (16%).
- The image below illustrates AI capabilities embedded into standard business processes such as computer vision (23%) and transfer learning (12%).
The Market Opportunity
- Nineteen percent of organizations use AI to increase employee learning and training, and 22% are completing tasks for open roles with automation tools and software, which in turn is saving employees time at 30% of respondents.
- Supply chain transparency for responsible labor practices and sourcing (26%) and DEI goals supported by AI-enabled processes (e.g., recruiting) (20%) are some of the ESG challenges respondents believe AI can address.
- The image below illustrates how organizations deploy AI to address labor shortages.
- The PwC AI Business Survey also indicated that 46% of AI adoption leaders and 24% of other companies intend to use AI to support business decisions impacting the workforce, including diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) measures.
- Publications related to computer vision accounted for almost one-quarter of all publications in 2021. Pattern recognition was the leading subject with more than half, while machine learning was a close second. The image below provides the number of AI publications by field of research.
- McKinsey reports that organizational investments in AI increased from 40% of digital budgets in 2018 to 52% in 2022. Within three years, 63% of respondents expect organizational investment to increase.
2.2 Status Quo/Current Processes
- This section will provide an overview of Good Maintenance Practices (GMP) along with information regarding training for plant operations maintenance. The information provided will be culled from the blogs and websites of training providers, and industry publications, where recent data is available.
Good Manufacturing Practices
- Currently, training in manufacturing environments is guided by the concept of Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), a system of "processes, procedures, and documentation" that ensures that products are consistently produced and controlled according to quality standards.
- GMP addresses quality management, hygiene and sanitation, building and facilities, equipment, raw materials, personnel, validation and qualification, complaints, documentation and recordkeeping, and inspections and quality audits. The ten principles of GMP can be accessed at this link.
- The main components of GMP are illustrated in the image below.
Current Training Programs — Plant Operations Maintenance
- A plant operator operates the "heavy machinery and equipment used in industrial and manufacturing processes." This can include preparing and positioning machinery before beginning work, monitoring controls to ensure safe operations, maintaining the machinery, and completing minor repairs. A larger list of responsibilities can be accessed at this link.
- Plant operations maintenance refers to the activities conducted to ensure that machinery and the facility remain in good working order.
- Training plant operators in maintenance results in reduced downtime, whether planned or unplanned, fewer safety issues, management flexibility, and improved employee morale and focus.
- Effective maintenance training requires "experience, technical knowledge, and excellent problem-solving skills."
- According to a blog post from Limble CMMS, the most popular approach to maintenance training is the "introduction - practice - verification" approach which will cover different permutations of the elements in the graphic below, as required by the environment at the time.
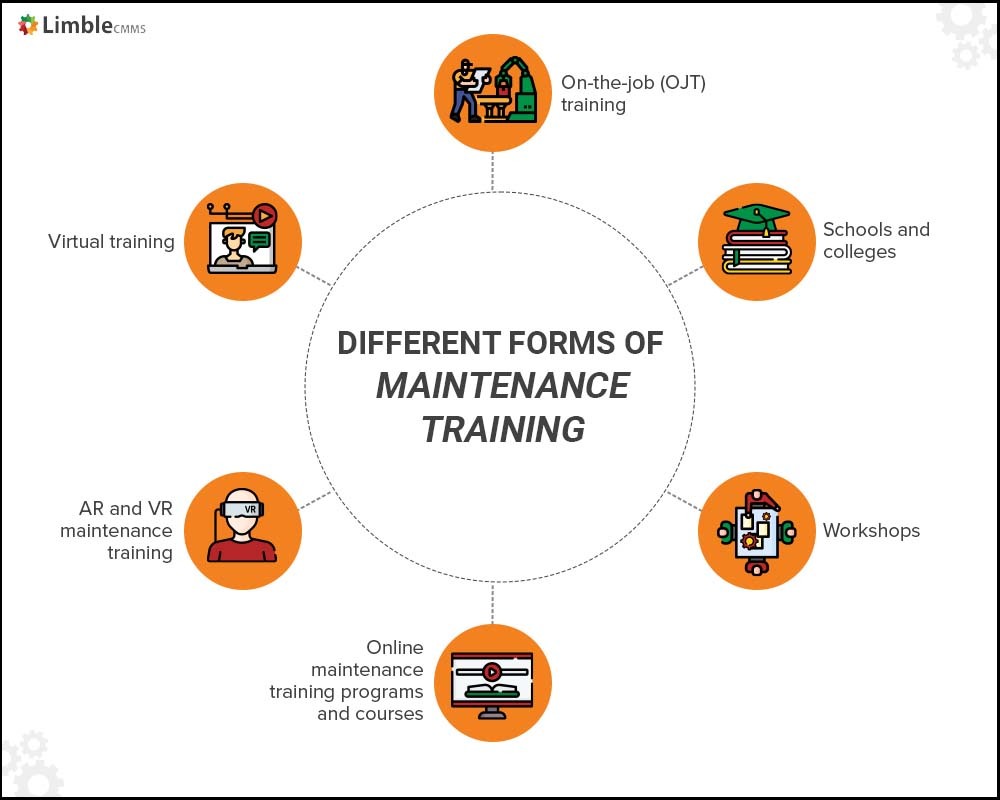
- Training can take place on the plant floor, in classrooms through strategic partnerships with schools, from internal and external workshops, via online maintenance training programs (e.g., TPC Training and Vector Solutions), using augmented and virtual reality, and virtually via collaboration tools such as Zoom.
- An effective maintenance training program comprises the ten elements in the graphic below, sourced from ReliablePlant magazine.
- The training needs assessment is broken down into six steps to develop a comprehensive maintenance plan for the company. The six steps are illustrated in the graphic below.
- When the training needs assessment is completed, job task analysis is required. This is aimed at identifying the critical skills required at sites, and also has six steps, which are illustrated in the graphic below.
- An employee skills analysis identifies how well the current team is equipped to handle plant maintenance. The next step, scoring and gap analysis/learning development mapping review the analysis to identify training opportunities and map out a plan.
- Depending on the size of the maintenance staff, a scalable Learning Management System can be considered to assist with scheduling and documenting training.
- An on-site training area may be designated for storing training materials to host training sessions. Effective training programs involve vendor qualification of a combination of organizations to ensure effective training.
- Training coordination and facilitation refer to assigning duties related to coordinating and overseeing training to someone internally or contracted to an external service provider.
- Training metrics cover agreement on the site training metrics to be tracked, identification of an owner for measurement and performance reporting, communication of KPIs throughout the organization, locating optimal points to metric tracking, and determining mechanisms that can measure the impact of the training initiative.
- Reassessment and training value identification refers to the review period for a training program. This can also include an employee skills assessment 18-24 months after the initial one to measure what has been successful, and what needs work.
Case Study — Multinational Food, Beverage, and Confectionary Company
- In 2020, a client of GP Strategies operating in over 80 countries and with annual sales of over $35 billion, was experiencing "abnormalities and defects" on the production line which were impacting the Overall Equipment effectiveness (OEE).
- Some of the issues experienced were derived from variations in the tasks being completed by operators, while procedures and other documentation needed to be updated. These combined to result in "poor defect identification and elimination" and a "lack of standard work" completed.
- The solution presented by GP Strategies included the development and implementation of "five rapid improvement operator care workshops" and the design of an "operator training program for a new production line."
- Details of the deliverables, hands-on training, toolkit, and train-the-trainer activities, as well as quantifiable data on the impact of the training conducted for the case study can be accessed at this link.
2.3 Buying Persona
- Precompiled B2B buying personas specific to the training use case for Edge AI Computer Vision are not publicly available. However, buyer personas for the manufacturing industry are available from Top Floor, a digital marketing agency, and from Thomas, an "industrial sourcing platform and marketing powerhouse."
- At Top Floor, purchasers/buyers, maintenance repair operators, design engineers, and OEM SMB CEO/President are presented as buying personas for B2B manufacturing.
- Buying behavior of purchases/buyers includes checking the internal approved vendor list, external searches, working with engineers to identify best-fit suppliers, price and delivery negotiation, and being concerned about "cost, lead time, quality and ongoing deliverability." The full profile, which includes job functions, challenges, and impact can be accessed at this link.
- Maintenance, Repair and Operations (MRO) Managers exhibit buying behavior such as buying planned purchases and emergency orders, small and large orders on a repeat and one-time basis, and ordering of replacement parts and consumable products. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- The buying behavior of design engineers includes a strong input into the buying process via recommendations on products by brand and part number, exhibits expertise and competence, not just a 'parroting' of information. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- OEM SMB CEO/President buying behavior includes a focus on bottom-line and cost-to-own partnerships, the final input into the buying process, research using search engines, and prioritizing of relationships with companies offering 'value-added' services. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- At Thomas, three manufacturing personas influencing the buying process are identified; Design Engineers, Procurement Managers, and MRO Managers. For each persona, Thomas provides their job focus, source of stress, job functions, buying behavior, background, and personality.
- The buying behavior of design engineers includes a strong input into the buying decision process and product recommendations by part and brand, exhibiting product confidence, and working primarily on desktop computers. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- Procurement managers' buying behavior includes working with engineers to identify suppliers and negotiate prices, delivery for parts and products, and working primarily on desktop computers and laptops. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- MRO Managers buying behavior includes buying for both planned purchases and emergency orders, completing small and large orders, acting as a combination of engineer and procurement personas, and working on almost any device. The full profile can be accessed at this link.
- Thomas advises that when creating a buying persona, researching current customers (what are they doing, what they want, what they look like, and what are their autopilot settings), creating distinct persona categories, and building campaigns based on the persona research are essential to the process.
2.4 Decision Makers
- According to TechTarget, the key decision makers for purchasing enterprise software are the individual controlling the budget and the person who has to approve the purchase.
- Due to organizational variances, these two roles may vary in terms of titles and numbers.
- The person controlling the budget, the economic buyer, may have veto power on the purchase while concurrently lacking the ability to authorize the purchase, particularly in large organizations where approval limits may be in place.
- The individual controlling the budget, or the economic buyer, "should be an IT professional," according to TechTarget because they will possess an understanding of the income sources supporting the business, how the technology will support revenue and profit, and how the new software will affect revenue and profits.
- Individuals approving the technology purchase, the technical buyer, can include "engineers, developers, analysts, administrators, architects and managers that evaluate whether a new service or product is fit for purpose."
- The role of the technical buyer is to interrogate whether the technology can deliver on the defined requirements and to determine if the investment is justified both for its capabilities and for the current organizational status.
- Staff from the purchasing department and the legal teams are also included in the purchase discussion to provide advice on contractual terms and conditions, along with environment, social, and governance (ESG) staff in larger organizations who sign off on the impact of the purchase on a social and environmental basis.
2.5. Venture Capital Investment
- Total venture capital investments into training for Edge AI Computer Vision is not publicly available, however, according to Pitchbook's Q3 2022 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Report the YTD summary for 2022 as of Q3 2022, there were 4,554 deals with total VC raised at $59.3 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 13.1%.
- At Crunchbase, data for computer vision startups indicate that a total of 723 startups have received approximately $8.5 billion in funding.
Triangulated VC Investment for Edge AI Computer Vision Training Use Case
- Based on an embedded rate of 23% across all industries for computer vision using AI, an estimated VC investment into this use case can be triangulated using the embedded rate for computer vision together with the total VC funding value and the number of organizations data from Crunchbase.
- Estimated Triangulated VC investment in Edge AI Computer Vision Training Use Case = $1.95 billion
- Calculation: $8.5 billion * 23% = $1.95 billion
- Estimated Triangulated VC investors in Edge AI Computer Vision Training Use Case = 166
Private Investment in AI
- Private Investment in AI-enabled HR Tech, according to the 2022 AI Index Report from the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial intelligence (HAI), amounted to $4.27 billion between 2017-2021. (See page 158)
- Private investment into AI-enabled industrial automation/network was $19.03 billion between 2017-2021.
2.6. Startups/Companies
- Nine startups/companies working in the Edge AI Computer Vision space with a training service or solution are provided in the attached spreadsheet.
- The startups/companies are Keyence, FLIR Systems, Cognex, Antares Vision Group, Omron Automation, Tulip, Osaro, and Landing AI.
- The majority of companies on the spreadsheet are derived from the industrial application industry map provided by the Edge AI + Vision Alliance, an industry partnership between "technology providers and end-product companies to accelerate the adoption of edge AI and vision in products."
- Invisible AI and Retrocausal are included on the Edge AI + Vision industrial industry map.
- The Alliance includes on its website an industry map of companies operating in systems and solutions for 11 industries, namely agriculture, communications and networking, consumer and mobile, defense and aerospace, healthcare, industrial, media and entertainment, office automation, retail, security and surveillance, and transportation.
- For industrial applications, the industry map is further subdivided into machine vision and robotics. Industry maps are also provided for enabling technologies such as components, enabling services and tools, and subsystems.
2.7. Additional Industries For Use Case
- In addition to manufacturing, Invisible AI offers its solution for use in industries such as medical devices, aerospace, electronics, automotive, appliances, and heavy equipment.
- Retrocausal offers its solution for use in the automotive, electronics, medical devices, defense, appliances, and medical training industries.
- Drishti offers its solution for use in the automotive, medical device, consumer/industrial, electronics, packaging, and aerospace and defense industries.
Research Strategy
For this research on a training use case for Edge AI Computer Vision, we leveraged the most reputable sources of information available in the public domain, including TechTarget CIO, PwC, IBM, Stanford, McKinsey, Edge AI + Vision Alliance, ReliablePlant and Pitchbook.
1. Selection Criteria - Use Cases
Precompiled data regarding the top 5 use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision for solving a skill or labor shortage is not publicly available. The use cases provided here were identified as top use cases for Edge AI Computer Vision by industry publications or practitioners, cross-referenced by articles on how AI can address labor shortages. Some of the actions addressing how AI can address labor shortages include Fast Company, Forbes, CEO World, and AI Authority.
2. Training Use Case - Due Diligence
Market Opportunity
Market values for AI-powered training programs for Edge AI Computer Vision targeted at training, on-demand coaching, or assessments of new or existing employees in a production environment are not publicly available. To determine this the research team searched for precompiled reports specific to Edge AI Computer Vision. As this proved unavailable, the research team sourced precompiled market reports for Edge AI and Computer Vision separately, the team then searched for precompiled AI training market reports, however, most of these did not have a narrow enough focus on Edge AI, Computer Vision, or a combination of the both to justify their use. Embed rates for computer vision across all industries along with AI adoption rates for manufacturing were sourced for other aspects of the market opportunity section, and these were used as the baseline data on which a triangulation of the potential estimated market value for AI-powered training/on-demand coaching, or assessments for Edge AI Computer Vision was completed based on precompiled market values for Edge AI. Below is an explanation of the methodology used in the triangulation.
Calculation:
- Market Value for Edge AI Software * AI Adoption Rate in Manufacturing = Edge AI in Manufacturing
- Edge AI In Manufacturing = $15.6 billion * 12% = $1.872 billion
- Edge AI in Manufacturing * Embed rate for Computer Vision (Across all Industry) = Estimated Market AI Training in Edge AI Computer Vision
- $1.872 billion * 23% = $430 million.
Information regarding related markets, AI adoption drivers and barriers, Ai user groups, and AI adoption rates are provided for context into the underlying demand for the product generally and specifically as it relates to the use case.
Buying Persona
Publicly available information specific to the training use case in Edge AI Computer Vision is not publicly available despite a review of the websites of Edge AI + Vision Alliance website and industry practitioners such as FLIR. Instead, we have provided data on the buying persona for manufacturing sourced from a digital marketing agency and a manufacturing platform.
Venture Capital
Data on VC investments into this use case was not publicly available, despite a review of the Edge AI + Vision Alliance website and the website of industry practitioners such as ReliablePlant and VC publications such as PItchbook. Instead, we have provided a triangulation based on data from Crunchbase regarding startups in the Computer Vision category. Private Investment data for fields related to the use case are also provided for context. Below is an explanation of the methodology used in the triangulation.
Estimated Triangulated VC investment in Edge AI Computer Vision Training Use Case
- Calculation:
- Total Funding for Computer Vision Startups * Embed rate for Computer Vision
- $8.5 billion * 23% = $1.95 billion
Estimated Triangulated VC investors in Edge AI Computer Vision Training Use Case